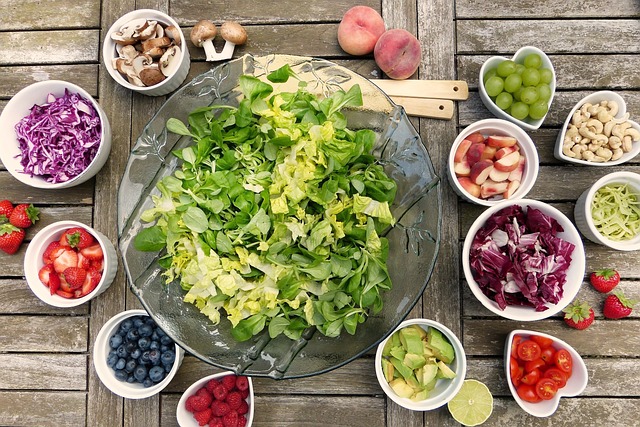
Staying healthy with antioxidant foods is not easy in today’s society and fast-paced lifestyle. When it comes to the overall body health and defense from diseases, nutritionists recommend the consumption of foods that contain antioxidants. The opposite of oxidants, antioxidants are substances that prevent free radicals within the body from altering cells and potentially leading to diseases. Consuming foods with high antioxidant value will assist in enhancing your immunity, skin, and in lowering the chances of getting diseases associated with aging. Below is a list of the best antioxidant foods you should not lack in your meal plan as follows.
The Benefits of Eating Antioxidant Foods
Eating antioxidant-rich foods offers numerous health benefits that can significantly improve your overall well-being. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Neutralize Free Radicals
Antioxidant foods help neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage. By reducing oxidative stress, antioxidants protect your cells and tissues from damage, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
2. Reduce Inflammation
Many antioxidant foods have anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is linked to a variety of health issues, including arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers. Consuming foods high in antioxidants can help reduce inflammation and promote better health.
3. Support Heart Health
Antioxidants such as flavonoids and polyphenols, found in foods like dark chocolate, berries, and nuts, have been shown to improve heart health. They help lower blood pressure, reduce bad cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular function, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease.
4. Boost Immune System
Antioxidant foods are rich in vitamins and minerals that support a healthy immune system. For instance, vitamin C, found in fruits like oranges and strawberries, boosts the immune system and helps the body fight off infections.
5. Promote Healthy Skin
Antioxidants like vitamins A, C, and E, which are abundant in foods such as spinach, blueberries, and nuts, play a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin. They protect the skin from damage caused by UV rays and pollution, promote collagen production, and reduce signs of aging.
6. Enhance Brain Function
Foods rich in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, have been linked to improved cognitive function and memory. They help protect brain cells from oxidative stress and may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
7. Improve Eye Health
Antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin, found in leafy greens like kale and spinach, are beneficial for eye health. They help protect the eyes from age-related macular degeneration and cataracts, preserving vision as you age.
8. Aid in Detoxification
Antioxidant-rich foods support the body’s natural detoxification processes. They help the liver function more efficiently, aiding in the removal of toxins and harmful substances from the body.
9. Maintain Healthy Weight
Many antioxidant foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains, are nutrient-dense and low in calories. They help you feel full and satisfied, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight and avoid overeating.
10. Prevent Chronic Diseases
Regular consumption of antioxidant foods is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases. The protective effects of antioxidants help reduce the risk of conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and certain types of cancer.
Best Antioxidant Foods for Your Diet
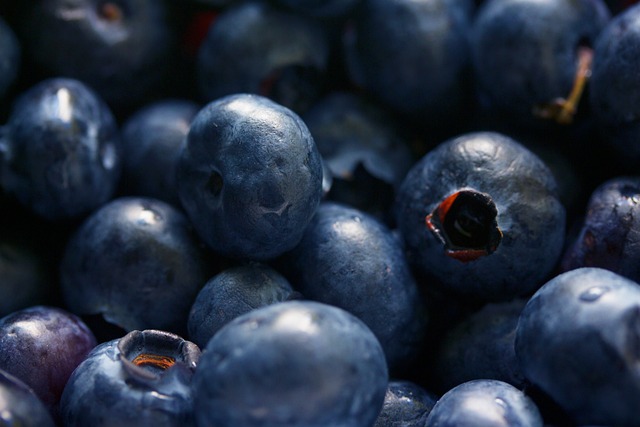
1. Blueberries
These berries are also known as a superfood, and with great cause. It is abundant in antioxidants, especially anthocyanins, which are responsible for the pigmentation of the fruits. These antioxidants reduce the effects of oxidisation and inflammation, which could potentially reduce the likelihood of heart disease and cancer. Also, blueberries are packed with vitamin C and K, dietary fiber, and other nutrients that make them healthy and tasty to munch.
2. Dark Chocolate
That is good news for choco-holics! Even though dark chocolate is sweet it contains great amounts of antioxidants, particularly flavonoids. It is important to note that these compounds can enhance the circulation of blood in the heart and lower the blood pressure as well. However, it should be recommended to use dark chocolate with the concentration of cocoa not less than 70%. It is advisable to consume it moderately since it is very calorie dense.
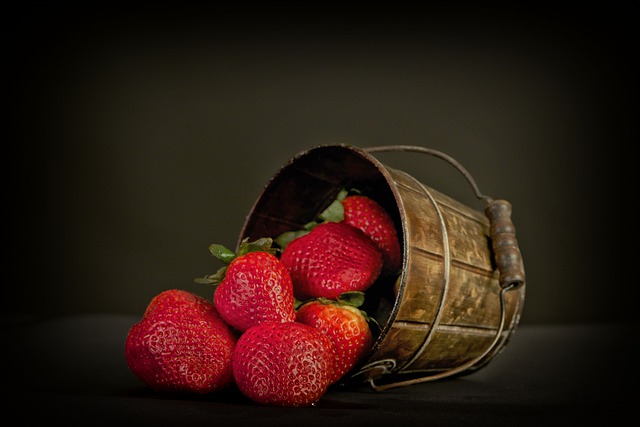
3. Strawberries
Strawberries are another fruits with high antioxidant content and I believe everyone enjoys eating strawberries with its juicy and sweet taste. It contains good amounts of Vitamin C and manganese and several antioxidant components including polyphenols. Strawberries have been endorsed for their anti –inflammatory and antioxidant contents and are also said to reduce cholesterol, blood sugar levels and promote heart health. Use them fresh or in milk shakes to garnish your favorite recipes or to accompany fruits and vegetables.
4. Kale
Kale is a type of cabbage that contains a lot of green leaves it is widely known to be having many benefits to the health of an individual. It contains tons of anthocyanins and flavonols such as quercetin and kaempferol that are good for managing inflammation and preventing heart diseases. It also contains essential vitamins such as the vitamins A, C, K and also fibers and calcium. Kale can be used in salads, soups or in blending as something to add in smoothies.
5. Spinach
Spinach is one of the vegetables that cannot be missing in the kitchen, as it is a vegetable with many nutrients and a high level of antioxidants. The vegetables are affluent in two chemicals that are particularly vital for the eyes, these are lutein and zeaxanthin. Iron and magnesium along with other nutrients like vitamins A, C, K and folic acid can be got from spinach. Spinach should be eaten as it is in salads, can be blended with different fruits to prepare smoothies, and can also be cooked and served as a vegetable.
6. Goji Berries
Goji berries which are also referred to as Lycium barbatum or wolfberries have for instance been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine. These are small, red berries which are rich in antioxidants such as vitamin C, zeaxanthin and carotenoids. This fruit is reported to enhance immune response, prevent certain eye diseases that are more common in old age and improve skin health. You can eat them in their dried form as a snack or you can include in cereals, yogurt or with tea.
7. Nuts
Antioxidant Foods are most abundantly found in nuts especially almonds, walnuts and pecans. They include vitamin E, which has antioxidant properties and assists in shielding the cells from damage, as well as healthy fats for the heart. Nuts are also rich in protein and fiber and, therefore, can be considered an ideal snack. It is also recommended that you take a small amount of nuts in order to enjoy the health benefits that nuts have to offer.
8. Green Tea
Green tea has been widely recognized as having numerous health benefits, primarily because of its potential antioxidants. This one holds catechins, including epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which help in lowering inflammation, raising metabolism, and preventing some diseases. It is recommended to take at least one cup of green tea daily as it contains high amount of antioxidants.
9. Broccoli
Broccoli is a green vegetable belonging to the group of cruciferous vegetables that are loaded with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. It has sulforaphane which is a compound that may posses anticancer properties. It is also rich in vitamin C which aids in the strengthening of the immune system, and fiber, which helps the digestive system. You can include broccoli in your meals by steaming, baking or incorporating it in stir fry preparations.
10. Red Grapes
The skin of red grapes is rich in antioxidants, including resveratrol, which has many benefits for the heart. Resveratrol has been associated with anti-inflammatory effects and decrease in chances of cardiac diseases. Red grapes are also rich in vitamins C and K and fiber. Red grapes can be eaten fresh or thrown into salads or can be taken as a snack.
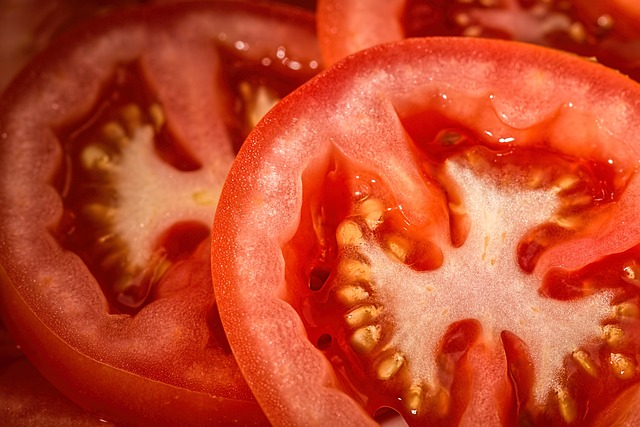
12. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a widely-used vegetable used in many recipes, a source of vitamins and minerals that contain antioxidants, that is, lycopene. Lycopene has also been linked to potential protective effects from heart disease and cancer. It is also a good source of vitamin C, vitamin K and potassium. Tomatoes can be consumed raw in salads or processed for use in sauces and soups; even tomatoes in their natural state are favored by many.
Take Antioxidant Foods in Your Daily Diet
From this discussion therefore, it can be noted that adding antioxidant containing foods is one of the easiest and most tasty ways of ensuring better health and well-being. Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, grains – every group provides its list of tasty and healthy foods. It is advisable to incorporate in your meals as many of these foods as possible since each of them has a distinct antioxidant. Just to remind you, choosing your food carefully, including lots of antioxidant-containing products, and leading a healthy way of life, you can guarantee your organism a sound health and a great deal of stamina.